(B) What Methods Have Been Used to Address the Erp System?
Growing companies eventually attain a point where spreadsheets no longer cut information technology. That's where enterprise resource planning software comes in: ERP systems collect and organize key business information and help organizations run lean, efficient operations, even every bit they aggrandize.
Most concern professionals have heard the term "ERP," but they may not know exactly what enterprise resource planning systems tin can exercise for their teams. We'll explain exactly what ERP is, how information technology works, what it can do for your business, how to choose the right solution and much more.
Read on for answers to just most any questions yous might accept nigh enterprise resource planning.
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
At its core, an ERP is an application that automates business processes, and provides insights and internal controls, cartoon on a cardinal database that collects inputs from departments including accounting, manufacturing, supply chain management, sales, marketing and human resources (60 minutes).
Once information is compiled in that fundamental database, leaders gain cross-departmental visibility that empowers them to analyze various scenarios, discover process improvements and generate major efficiency gains. That translates to cost savings and better productivity equally people spend less time digging for needed data.
ERP software that's tailored to run across the needs of an individual business pays major dividends, making these systems a disquisitional tool for companies across industries and of all sizes. Many of the world's best-known and most successful firms have leaned on ERP for the concluding quarter century. Now, this software tin be configured and priced to run across the needs of all-size businesses.
Put just, an ERP system helps unify people, cadre business organisation processes and technology beyond an organisation.
Video: What is ERP?
Fundamental Takeaways
- ERP is critical business concern software that collects information from various departments in a common database, enabling leaders to monitor the pulse of a company using a unmarried vision of reality.
- Enterprise resources planning systems unify critical concern functions like finance, manufacturing, inventory and order management, customer communication, sales and marketing, project management and human resources. 1 major feature is detailed analytics and reporting on each section.
- ERP can generate major fourth dimension and financial savings by providing arrangement-wide visibility that spotlights inefficient manual processes and reveals opportunities for growth.
- There are several deployment models for ERP software, including on-premises, cloud and hybrid. While cloud ERP has get extremely pop in recent years, which approach is best depends on company needs.
- Businesses should make certain they empathize the capabilities, implementation models, integration requirements and total cost of ownership of a brusque list of suppliers before picking a winner.
ERP Explained
Enterprise resource planning — a moniker coined past inquiry house Gartner in 1990 — tin can be a disruptive concept because ERP is not a standalone application. While ERP is a category of business software, ERP systems incorporate various modules, each addressing a specific business organisation requirement. For instance, products-based companies typically have modules for accounting, inventory and order management, customer relationship management (CRM) and, if they produce or assemble products, manufacturing. Services businesses may turn to modules for bookkeeping, project direction, professional services automation and CRM.
Each module pulls data from and pushes information into the central database that is a central component of an ERP system. This mutual data repository provides visibility into all departments and thus allows leaders to evaluate and compare the business organisation functioning of different areas and empathise the full touch of decisions. Information technology as well powers other ERP benefits, similar process automation, improved internal controls and smarter business concern intelligence.
Why Is ERP Of import for Businesses?
ERP systems have become table stakes for businesses looking to apply resources wisely. They tin can assistance leaders reallocate homo and financial capital letter or build more efficient core business processes that salve money without sacrificing on quality or performance.
An ERP is as well an asset when it comes to planning and coordination. Employees tin can see current available inventory and customer orders in detail, then compare supplier purchase orders and forecasted future need. If necessary, they tin make adjustments to head off bug. ERP software improves communication and collaboration every bit well because workers can check on the status of other departments to guide their own decisions.
As a comprehensive source of data, an ERP organisation also provides a host of reports and analytics that tin can be deviation-makers for the business organisation. Turning a vast trove of information into charts and graphs that clearly illustrate trends and assist model possible results is an ERP capability executives find invaluable.
How Does an ERP System Work?
ERP systems piece of work past using a defined, standard information structure. Information entered by one department is immediately bachelor to authorized users across the business. This uniform structure helps keep anybody on the aforementioned page. For example, say a local food distribution chain has multiple locations that often share stock and personnel. Every bit quality, sales and employee information from these sites is fed into the ERP organisation, it's formatted to point which location it comes from.
Real-time information is then woven into business processes and workflows across departments. Leaders tin can see if one location is doing significantly meliorate at avoiding spoilage than a sister site a few towns over and work to figure out why, while operations can make sure staffing levels marshal with traffic patterns. Finance can compare sales to rents to help executives decide whether to consolidate.
ERP systems deliver the near value when a company has modules for each major business concern function and ensures timely, accurate information entry. And, the more stakeholders have access, the better.
When a company uses business concern systems from multiple vendors, integrations are generally possible to make data automatically flow into the ERP. This real-time information can then be used throughout the ERP instance to benefit any process or workflow.
How Tin ERP Improve or Help a Business?
ERP enables companies to identify areas of the concern with room for improvement or opportunities for expansion. User uptake is key: The more employees with admission, the more likely teams will spot problems, whether a spike in demand for a certain product, late shipments from a supplier or an impending greenbacks menses crunch. Employees can then proactively mitigate the outcome to the extent possible.
Executives are generally focused on outcomes — using information to achieve objectives, like increasing efficiency, reducing costs and responding to changing consumer needs or market conditions.
For business units, ERP software tin automate many error-prone tasks, like account reconciliations, customer billing and order processing, and provide the information teams need to operate more efficiently.
But the real beauty of ERP is that it tin requite both a 10,000-foot view of the company'south health and detailed insights into a specific process or KPI by not only storing and organizing data, simply identifying patterns and flagging anomalies that require investigation. Try that with a spreadsheet.
Other business upsides:
Admission to data from anywhere: Employees no longer need to shuffle through piles of papers or files scattered across a desktop. With cloud-based ERP, a warehouse manager tin log in from a mobile device while on the shop floor, or a salesperson tin can check inventory while at a client site.
Information is always up-to-date: Because the ERP system is continually receiving data from various departments, it's updated immediately as inventory is pulled, a payment is posted or emails are sent to customers. This provides a major reward because determination-makers are basing their choices on up-to-the-minute data.
Business decisions based on the same data: With a common database, all determination-makers are on the same page. There are no duplicate or conflicting sources of information, and companies take the ability schedule and distribute dynamic reports automatically. Demand more depth? Underlying data can exist accessed merely by clicking the written report.
Who Uses ERP?
Companies across every manufacture, with diverse business models, have realized the benefits that come up with ERP. Flexible solutions with extensive functionality tin cater to a wide variety of organizations and requirements.
Industries that count on ERP to run their businesses include:
- Advertizing and digital media
- Dress, footwear and accessories
- Campus stores
- Consulting
- Education
- Energy
- Financial services
- Food and drinkable
- Health and dazzler
- Healthcare and life sciences
- IT services
- Manufacturing
- Media and publishing
- Nonprofit
- Professional person services
- Restaurants and hospitality
- Retail
- Software and technology
- Transportation and logistics
- Wholesale distribution
Roles & Users
Within those organizations, a number of job functions benefit from ERP, including merely non limited to:
-
Finance/accounting: The bookkeeping team is often the first adopter. This group will track and study on all transactions and other financial information in the organisation, including accounts payable (AP), accounts receivable (AR) and payroll. With ERP, financial planning and analysis (FP&A) experts — whether a separate role or part of the accounting department — can plow comprehensive financial data into forecasts and reports on revenue, expenses and greenbacks flow.
-
Supply concatenation: Employees focused on operations, a grouping that includes purchasing agents, inventory planners, warehouse managers and senior supply chain leaders, rely on the ERP system to ensure a smooth and continuous flow of goods from supplier to client. They count on authentic, detailed information provided by the arrangement to optimize inventory levels, prioritize orders, maximize on-time shipments, avoid supply concatenation disruptions and identify inefficient or transmission processes.
-
Sales and marketing: An ERP solution can increase the productivity of and drive better results for your sales team by automating lead management and monitoring the interactions prospects have with your company. Reps tin document discussions and modify the status of prospects as they motion through the sales funnel. Using those aforementioned records, marketing can automate and manage outreach across all channels, from e-mail to display ads to social media, and measure the effectiveness of those messages and channels to amend allocate its budget.
-
Human being resource: The HR department tracks all employee information and broader workforce trends in the ERP. It can rapidly find contact data, bounty and benefits details and other documents for each employee. HR tin also monitor metrics similar retention by department, average pay by title, promotion rate and other metrics to better classify its ain staff and assist line-of-business managers.
When You Demand ERP
While ERP software was initially designed for enterprises — every bit the name indicates — today'due south deject-based software-as-a-service (SaaS) ERP offerings have lowered barriers to entry and helped countless emerging and midsize companies increment their efficiency, visibility and, in plow, profitability.
So how practise yous know if ERP is for yous?
All companies should regularly review their current technology and ask: Is our applied science helping — or holding usa back? When outdated or inadequate systems introduce inefficiencies, muddied the information waters or can't support changes the business wants to make, it'due south time to look for a new solution.
Other signs it's time for a change: Inaccurate data, a lack of integration amid systems, high fault rates and over-reliance on email and spreadsheets. Although there are costs that come up with purchasing and deploying ERP software, it often delivers a quick render on investment. And, there's help available for those looking to build a business organisation case.
12 Benefits of ERP Systems
Today's ERP solutions have rich characteristic sets that bring countless benefits to businesses. While what an individual firm sees as the greatest value of this applied science will vary, here are key universal advantages ERP delivers:
1. Toll savings: Perhaps the biggest value proposition of ERP systems is they can save your organization coin in a number of ways. Past automating many simple, repetitive tasks, you minimize errors and the need to add employees at the same rate as concern growth. Cantankerous-visitor visibility makes it easier to spot inefficiencies that bulldoze up costs and leads to ameliorate deployment of all resources, from labor to inventory to equipment. And with cloud ERP, companies may quickly come across incremental value from the software, over and higher up what they're spending.
2. Workflow visibility: With all workflows and information in one place, employees with access to the organisation can see the status of projects and the performance of dissimilar concern functions relevant to their jobs. This visibility may be particularly valuable to managers and leaders, and it's far faster and easier than searching for the right documents and constantly request colleagues for updates.
3. Reporting/analytics: Data is useful just if companies can analyze and understand it, and an ERP helps with that. Leading solutions have impressive reporting and analytics tools that allow users to not only track KPIs, but brandish any metrics or comparisons they can dream up. Since an ERP is all-encompassing, it tin assist a concern empathise how a change or trouble with a process in ane department affects the remainder of the company.
four. Business insights/intelligence: Because ERPs can access existent-fourth dimension data from across the company, these systems can uncover impactful trends and provide all-encompassing business concern insights. This leads to improve decision-making past organizational leaders who at present have easy admission to all relevant data.
v. Regulatory compliance & data security: Financial reporting standards and governmental and manufacture-specific data security regulations modify frequently, and an ERP can help your company stay safe and compliant. An ERP provides an inspect trail by tracking the lifecycle of each transaction, including adherence to required approval workflows. Businesses may also reduce the take a chance of errors and related compliance snafus with automation. ERP software provides financial reports that comply with standards and regulations, and SaaS applications are well-equipped to assist companies with PCI-DSS compliance.
6. Chance management: ERP engineering science reduces risk in a few means. Granular access control and defined blessing workflows tin can strengthen financial controls and reduce fraud. Additionally, more-accurate data heads off mistakes that could lead to lost sales or fines. And finally, the power to run into the condition of the unabridged operation enables employees to speedily handle risks posed by business disruptions.
7. Data security: ERP providers empathise that your system houses critical, sensitive data and take necessary steps to ensure information technology is secure. This diligence is more important than ever every bit the volume and scale of cyberattacks increase. Deject ERP software, in particular, uses cut-border security protocols to ensure your company doesn't fall victim to a damaging attack.
eight. Collaboration: Employees are nigh constructive when they work together. ERP solutions make information technology easy to share information — like purchase orders, contracts and client-support records — among teams. It knocks down walls between departments by giving employees advisable admission to real-time data on related business organisation functions.
9. Scalability: The correct ERP system will be scalable and flexible enough to meet your company'due south needs today and for the foreseeable future. Cloud systems in particular adapt to minor and major operational changes even equally the amount of data the organization captures and demand for access increase.
10. Flexibility: While ERP software helps businesses follow best practices, it also offers the flexibility to support unique processes and objectives. The system gives administrators the ability to build out company-specific workflows and create automatic reports important to different departments and executives. An ERP enhances your system'due south innovation and inventiveness.
xi. Customization: While most companies discover that modern ERPs back up their businesses "out of the box," some firms need to add to the extensive built-in functionality. If you have a lot of specialized processes, look for an extensible arrangement that allows your integrator or IT staff to write code that adds needed features, or that tin can integrate with homegrown or legacy solutions. However, before going the custom road, take a shut look at your processes — the prebuilt functionality and configurations modern ERP solutions back up are based on all-time practices gathered from thousands of companies. Aim to minimize customizations.
12. Customer & partner management: An ERP can strengthen a company'due south partner and customer relationships. It tin can provide insights on suppliers, shipping carriers and service providers, with the cloud enabling fifty-fifty meliorate, more convenient information commutation. When it comes to customers, the solution can track survey responses, support tickets, returns and more so the organisation can go on its finger on the pulse of customer satisfaction.
6 Disadvantages of ERP Systems
Despite all the value ERP brings, there are challenges businesses may meet. Many of these can exist avoided by preparation and choosing the right supplier partner.
1. Organization toll: Considering they were expensive to purchase, implement and maintain, early on ERP systems were attainable only to large companies. Even so, that hasn't been the case for ii-plus decades. While ERPs still require a time and financial investment, the engineering has become much more affordable thanks to both SaaS systems that charge a recurring fee and more solutions designed for pocket-sized and midsize businesses entering the market. Organizations tin utilize tools to calculate estimated savings after 1 and three years, for instance, to find out when returns will surpass costs.
two. Demand for training: Similar any new tech, ERP has a learning curve. Anyone who will employ the software — that is, ideally, well-nigh or all of your employees — requires some level of training. Although at that place may be resistance at start, that should fade away as people realize how much the applied science will help them. Newer systems that receive frequent updates are more than intuitive and user-friendly, reducing training requirements and increasing adoption.
iii. Data conversion costs: When moving to a new ERP, you may need to convert some information into a format that's compatible with the new platform. This tin can lead to unexpected costs and delays, so review your databases, and piece of work with your IT team or an integration partner to place potential data compatibility issues early on. And so, you can factor conversion efforts into the ERP implementation plan.
4. Complexity: An ERP system is loaded with features, and that can be daunting to your workforce. Just the software bachelor today is far easier to utilise than legacy systems considering vendors have focused on improving the user experience. Additionally, employees demand access to just the modules and dashboards required for their jobs, which can make information technology more approachable. Thorough grooming should atmosphere concerns about complexity.
five. Maintenance: In the past, maintenance was a large expense that deterred lower-revenue businesses from adopting ERP. Non merely did a company need an Information technology staff to handle patches, security and required system upgrades, information technology frequently had to pay the vendor or a tertiary-party service provider for its expertise. This is less of a business concern with a SaaS system because the provider takes care of all maintenance and regularly moves all customers to the latest version — and it's all built into the subscription cost. Companies concerned about maintenance should thoroughly vet a potential supplier to ensure it offers a true vendor-managed SaaS system.
6. Doesn't solve process and policy bug: If you take error-prone or inefficient processes, an ERP won't necessarily ready them, even though it may increase accurateness. It can, all the same, uncover problems in your operations and help y'all brainstorm better ways to do business. The aforementioned goes for policies that hold the organization dorsum — it'southward up to you to adjust those and so configure the system to support better ways of doing concern.
5 Key Features of ERP systems
In that location are a few fundamental features that make an ERP system an ERP system and distinguish it from other types of software. Those include:
1. Common database: Many of an ERP's advantages stem from a common database that allows organizations to centralize information from numerous departments. This single source of real-time information eliminates the need to manually merge split up databases, each controlled by the business functions they serve. A common database enables a consistent, cross-functional view of the visitor.
2. Consistent UX/UI: Beyond departments and roles, everyone uses the same user interface (UI) and has a similar user experience (UX) with an ERP. Modules for inventory direction, HR and finance all take the same look and feel and shared functionality. This increases the software's adoption rate and tin make it easier for staff to move between departments. A consistent UX and UI likewise result in efficiency gains considering users can rapidly find and understand information from all corners of the business organisation.
three. Business organisation process integration: An ERP must be able to back up and integrate the processes that make your business successful, whether related to accounting, supply chain management or marketing. The correct platform will have the power to unify a various fix of processes — connecting workflows that play crucial roles in the company's success boosts productivity and visibility, and that translates to lower costs.
4. Automation: Another bones feature of ERP software is the ability to automate repetitive tasks like payroll, invoicing, order processing and reporting. This reduces transmission, and sometimes duplicative, data entry, saving time and minimizing errors. Automation frees up your staff to focus on value-added work that takes advantage of their special cognition and skills.
5. Information analysis: Ane of the most valuable aspects of an ERP is that information technology breaks down information siloes. When yous can mix and match data from merely almost whatever part of your business concern into insightful reports, y'all uncover areas that are performing exceptionally well and those that are failing to run across expectations. Leaders tin analyze problems and go to work resolving them correct away.
Types of ERP Deployment Models
Various ERP deployment models accost the needs of different organizations. Hither'southward an explanation of how each works and cardinal differences:
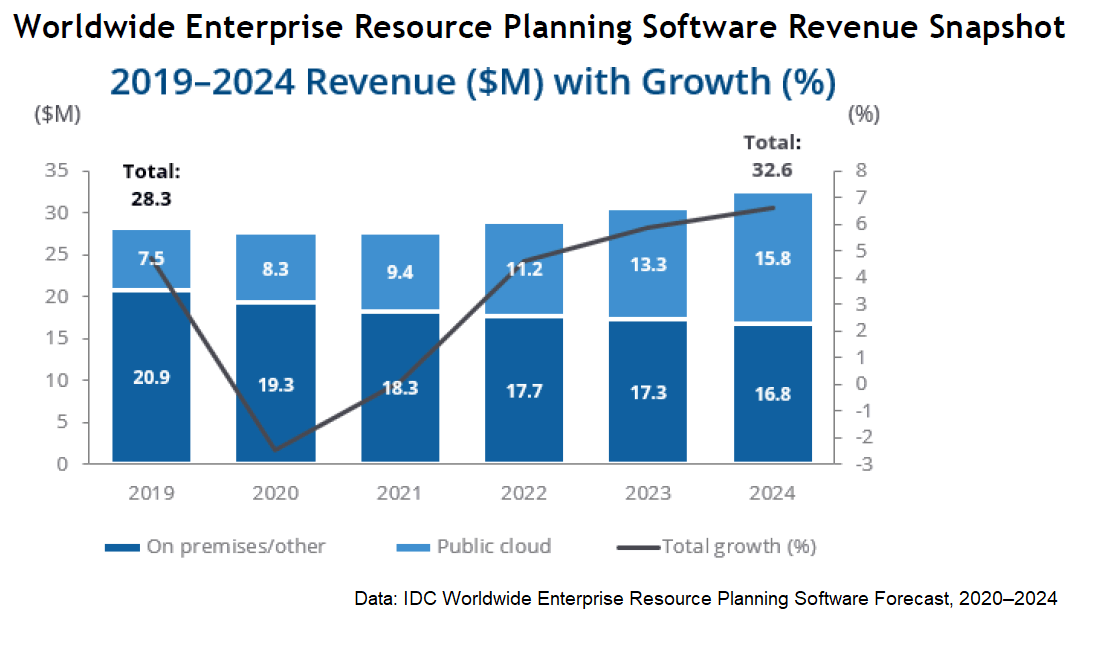
On-premises ERP: With an on-premises organisation, the business runs the software on servers it owns and is responsible for security, maintenance, upgrades and other fixes. Upkeep usually requires in-business firm IT staffers with the required expertise. For many years, on-premises ERP was the only selection, simply the popularity of this deployment model has declined rapidly in contempo years, and market-watcher IDC predicts continued declines (see chart, below).
Cloud-based ERP: Cloud-based ERP runs on remote servers managed by a third party. Users typically admission a cloud ERP through a web browser, giving them greater flexibility — they tin can dig into information and reports from anywhere with an internet connection. There are multiple deployment options for cloud ERP, including unmarried-tenant and multi-tenant.
A single-tenant solution is a separate instance of the ERP used by but one company that doesn't share server infinite. This setup can give the client greater control over the software and allow for more customizations, but information technology also creates more work for the business. With a multi-tenant solution, a number of organizations use the same software example and hardware. Most SaaS ERP solutions are multi-tenant, with the software vendor handling all updates and upgrades and regularly moving customers to the latest version. This reduces the need for an in-house IT team and ensures that the company always has the well-nigh up-to-date, secure example of the software.
IDC estimates that employ of deject-based ERP will more than double betwixt 2019 and 2024.
Hybrid ERP: Hybrid ERP combines elements of on-premises and deject deployments. One hybrid approach is two-tier ERP, where a corporation keeps its on-premises ERP in identify at headquarters but employs deject systems for subsidiaries or certain regional offices. These cloud solutions are and then integrated with the on-premises system. Other companies may turn to deject solutions for certain concern needs while sticking with their on-premises systems for other functions. Either way, the cloud systems must be linked to the on-bounds platform to ensure a steady period of information — oft easier said than done.
Open-source ERP: Like other open-source applications, open up-source ERP is an inexpensive, and sometimes free, alternative that'southward suitable for some companies. Many open-source ERP providers allow businesses to download their software for free and charge a low annual fee only if the customer wants cloud access. These solutions have improved, with more modernistic spider web-based interfaces and a growing number of modules, simply companies demand to understand what they're taking on with an open-source ERP. Support from the provider volition be minimal, and configurations and organisation improvements tend to fall on the client. That means you need technical staff with a deep knowledge of how to develop and configure the software.
ERP Systems by Business organisation Size
Acquirement and/or number of employees is merely ane factor shaping your ERP requirements. No single arrangement will exist best for every small, midsize or large company, respectively. But there are features specific to these segments as well as favored deployment models.
Pocket-sized-business organization ERP: Small firms should map out their requirements before starting a search to avoid software that has far more than functionality than they need. This will keep costs downwardly and reduce the training required for employees. Notwithstanding, the system should accept the power to scale upwardly and support new initiatives over time as well as a straightforward implementation procedure. That'southward why deject ERP is generally the best option for pocket-sized businesses — information technology has lower upfront costs, a faster setup timeline and less need for technical resources compared with on-premises or hybrid options. The deject offers the scalability to meet the business's needs equally it grows, and the right provider can supply modules and features as required.
Midsize-business ERP: Midsize companies should need a platform that tin can support all its business functions with specialized modules and, like smaller firms, select a vendor capable of scaling to run into future needs.
Because many midsize organizations lack big IT teams, deject ERP software is very pop in this segment besides. In add-on to lower initial expenses, leading SaaS solutions can be more convenient for a company that has limited technical expertise. However, midsize businesses that require numerous customizations or must follow regulatory policies that bar them from storing information in the deject may opt for on-premises deployments or a hybrid approach. This group is more likely to have the financial and homo capital letter to support this model than modest businesses.
Enterprise ERP: Enterprises should opt for software that can support all components of their businesses, which could quickly sparse the listing of contenders. Corporations crave systems that can capture, process and interpret a vast amount of information and handle the demands of many business concern units.
On-premises and hybrid ERP that combines cloud and on-premises solutions are most common with enterprises, simply because they may have adopted ERP before pure cloud systems were available. While moving a massive ERP to the deject can be a time- and resource-intensive undertaking, more of the earth's largest companies are taking that step as they realize the benefits and try to put themselves in a better position for future growth. Some enterprises have also deployed 2-tier ERP, which uses a SaaS solution for parts of the business concern and integrates with the primary on-premises ERP.
ERP Modules
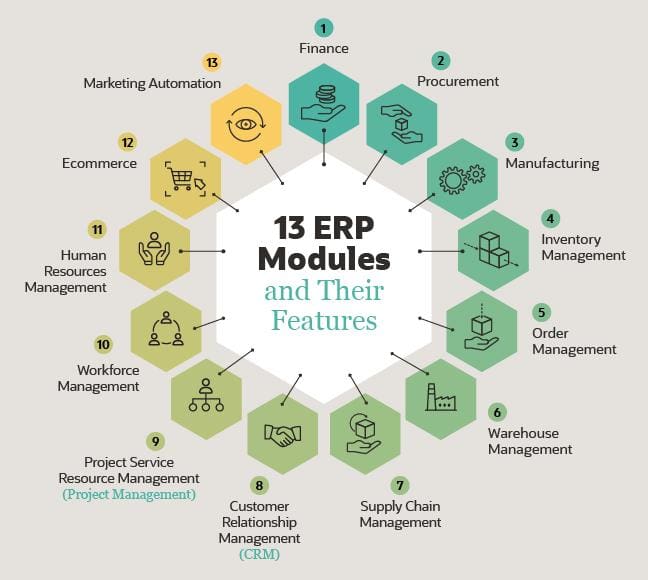
An ERP comprises a number of dissimilar modules — bundles of features tailored for diverse aspects of the business, including dorsum- and front-function roles. Here's a quick breakup of the nearly widely used ERP modules.
Finance: A finance module, the foundation of just about every ERP arrangement, manages the general ledger and all financial data. Information technology tracks every transaction, including accounts payable (AP) and accounts receivable (AR), and handles reconciliations and fiscal reporting.
Procurement: The procurement module manages purchasing, whether raw materials or finished goods. It can automate requests for quotes and buy orders and, when linked to demand planning, minimize overbuying and underbuying.
Manufacturing: Manufacturing tin be complicated, and this module helps companies coordinate all the steps that get into making products. The module can ensure product is in line with demand and monitor the number of in-progress and finished items.
Inventory management: An inventory management module shows current inventory levels downwards to the SKU level and updates those numbers in real time. It also measures cardinal inventory-related metrics. Whatsoever products-based company needs this module to optimize stock on-hand based on electric current and forecasted demand.
Order management: This application monitors and prioritizes customer orders from all channels as they come in and tracks their progress through delivery. An order direction module tin speed fulfillment and delivery times and ameliorate the customer experience.
Warehouse management: A warehouse management module directs warehouse activities like receiving, picking, packing and aircraft. Information technology can generate fourth dimension and cost savings in the warehouse by identifying more efficient means to execute these tasks.
Customer human relationship direction (CRM): CRM is a popular module for businesses in a wide range of industries. It tracks all communications with clients, assists with lead management and tin enhance customer service and boost sales.
Professional services automation (PSA): Services businesses often use a professional person services automation (PSA) module to program and track projects, including the time and resource spent on them. It can simplify client billing and encourage collaboration among staff members working on a project.
Workforce management (WFM): A workforce direction (WFM) module keeps rail of omnipresence and hours worked, and some tin can too manage payroll. This tool can tape absence and productivity past department, team and individual employee.
Human resources management (HRM): A human resource direction (HRM) or man upper-case letter management (HCM) module version of a WFM module. It keeps employee records with detailed information, like available PTO and operation reviews, and tin can tease out workforce trends in various departments or demographics.
Ecommerce: An ecommerce module allows retailers and brands to manage the back- and forepart-ends of their online stores. They can change the site look and experience and add and update product pages with this awarding.
Marketing automation: This module manages marketing efforts beyond all digital channels — email, web, social — and enables organizations to optimize and personalize their messaging. A marketing automation tool tin boost leads, sales and client loyalty.
ERP Best Practices
Most ERP software is congenital around established all-time practices. The software provider designs workflows and functionality based on its experience working with hundreds or thousands of customers and encourages every bit much conformity as possible, though there is ofttimes flexibility to adjust processes.
Adhering to industry-standard best practices has major business advantages. Companies often observe that they improve and modernize their processes, and in turn maximize operational efficiency and avoid falling behind competitors. Observing best practices also helps companies comply with central financial standards. Leading ERP vendors offer vertical-specific versions of their software that incorporate business practices that are best for each sector.
ERP Implementation
ERP implementations are of import projects that, without proper grooming, can eat up a lot of fourth dimension and money. Exactly how long this project takes and how much information technology costs will depend on many factors, including deployment model, implementation strategy, complication of the organisation, size of the company and resources dedicated to it.
This ERP implementation checklist should aid guide you.
7 Stages of Implementation
As with other initiatives, companies can avoid major challenges past taking the time to create a detailed implementation program. Preparation pays off.
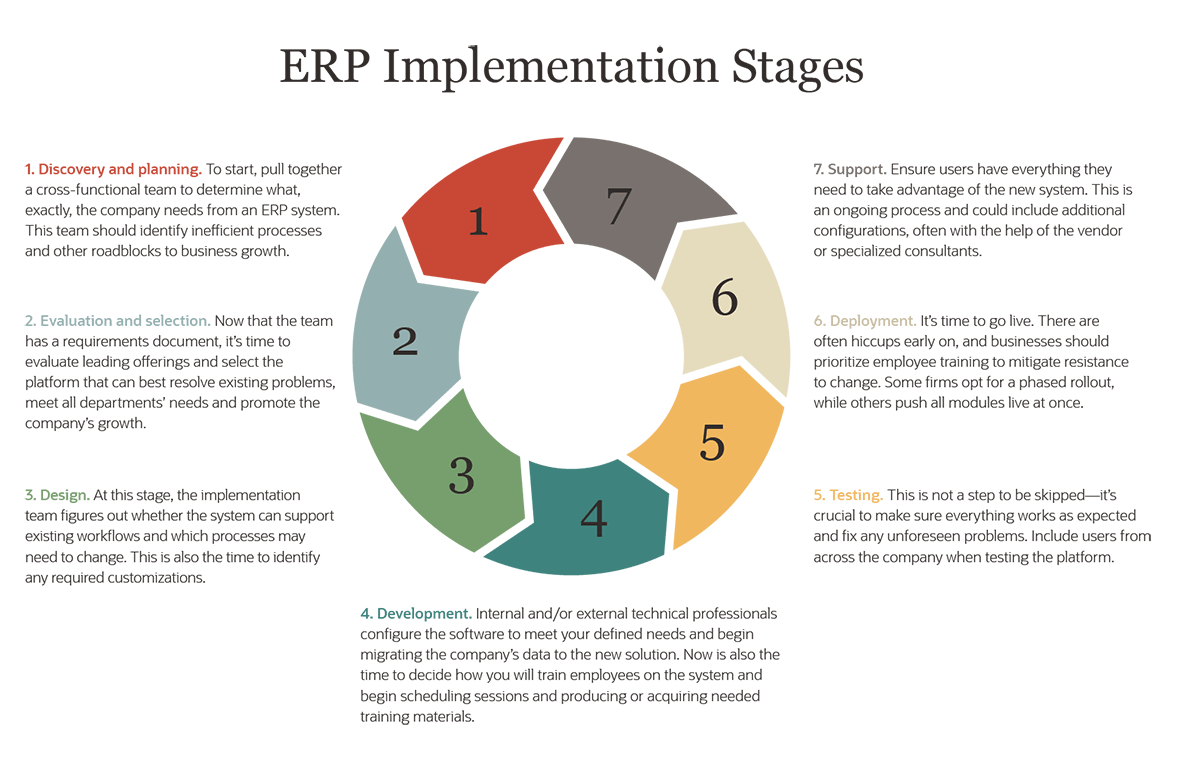
Here are the vii key stages of an ERP implementation:
1. Discovery and planning: To get-go, pull together a cross-functional team to determine what, exactly, the company needs from an ERP system. This squad should place inefficient processes and other roadblocks to business organisation growth.
2. Evaluation and option: Now that the team has a requirements document, it's fourth dimension to evaluate leading offerings and select the platform that can best resolve existing problems, meet all departments' needs and promote the company's growth.
three. Blueprint: At this stage, the implementation team figures out whether the organization tin back up existing workflows and which processes may need to modify. This is also the time to identify any required customizations.
4. Development: Internal and/or external technical professionals configure the software to meet your defined needs and begin migrating the visitor's data to the new solution. Now is too the fourth dimension to decide how y'all will train employees on the system and begin scheduling sessions and producing or acquiring needed training materials.
v. Testing: This is not a stride to be skipped — information technology's crucial to brand sure everything works every bit expected and fix any unforeseen problems. Include users from across the company when testing the platform.
6. Deployment: It's fourth dimension to go live. At that place are ofttimes hiccups early on, and businesses should prioritize employee training to mitigate resistance to alter. Some firms opt for a phased rollout, while others button all modules live at one time.
7. Support: Ensure users accept everything they need to have advantage of the new organization. This is an ongoing process and could include additional configurations, frequently with the help of the vendor or specialized consultants.
Implementation All-time Practices
Consider these implementation best practices as y'all begin your project:
- Secure an executive sponsor: Such a far-reaching and critical project needs support from top leadership — ideally multiple executives who stand for unlike business units.
- Outset planning early: Leave aplenty time to map out ERP requirements, prioritize tasks, place processes you want to improve and evaluate several vendors.
- Communicate and collaborate: Communication is essential throughout the project, from discovery through development, deployment and beyond. Solicit input from employees from across the organization to brand sure the software volition help anybody in their mean solar day-to-day jobs.
- Set up reasonable expectations: Establish a clear timeline for each stage of the project, along with expected costs and time required of specific employees. Make sure stakeholders understand there will be bumps forth the way.
- Cull the best KPIs: Collaborate with a diverse group of business organization leaders to select the KPIs about valuable to the company that the system should track. Keep the organisation'due south big-picture goals in mind.
ERP Integration
Virtually every organization because an ERP implementation volition take systems in place that could be replaced by modules of the ERP under consideration. As such, part of adopting an ERP system involves determining which existing systems will be replaced, which must be integrated and which will be left to stand on their own.
Recall, the more than information that'southward fed into the ERP, the more value you become from your investment, so avoid leaving systems to stand up apart from the ERP.
Deciding when to integrate existing systems with your ERP and when to supersede those systems with modules from your ERP vendor comes down to iii considerations:
Beginning, is the existing system doing the job y'all need it to do? If not, so there's a adept case to be made for using the relevant module offered past your ERP vendor.
2nd, if the existing system is a keeper, is there a connector available from the ERP vendor, the existing organisation vendor or a third political party to go data flowing between the ERP and your existing system? And if then, how adept is it? Data migration is complex. These connectors tin practise a decent task of integrating systems from different vendors, but quality and delivery to updates tin can vary. Remember: Upgrades to either the ERP or the standalone system tin pause connectors or require rework. In the worst example, the lack of a new connector could derail upgrade plans completely.
3rd, if a connector exists, does information technology operate in real time and keep all necessary information flowing to and from each system? Some connectors operate in existent fourth dimension, others synch upwardly systems on a daily or weekly basis. Some move only a limited set of data betwixt systems, and some work in only ane direction — say, from an inventory management system into the ERP. If your squad has washed extensive custom configurations, some data types might non be known to the connector.
If yous decide to proceed all-time-of-breed systems and integrate them with your chosen ERP, realize that verifying the right performance of connectors will become part of every upgrade cycle and that extensive customizations can cause issues. If your goal is to automate back-function functions, real-time, bidirectional performance is of import. Ensure you lot have the expertise, either in-house or through a partner or supplier, to keep data flowing.
Cost of ERP
The toll of an ERP projection varies widely depending on vendor, modules and deployment model. Generally speaking, full costs tin can range from less than $10,000 per year to millions of dollars annually. ERP systems are priced with the needs of the target audition in mind, so those built for emerging and high-growth businesses will be more affordable than those used past Fortune 500 enterprises.
Cloud-based ERP, and specifically multi-tenant SaaS options, usually accept lower upfront costs than on-premises software because there's no hardware to buy nor organisation experts to hire. With a SaaS solution, the vendor takes care of budget and charges its customers an almanac fee, often on a per-user basis.
The cost of ERP will also vary based on which modules you need. Solutions may come up with core functionality for finance and bones inventory/society management, but calculation complementary modules brings an additional fee.
With on-premises software, companies purchase a perpetual license that's more than expensive, but information technology's a i-time expense. Every bit with SaaS, the price of this software volition vary based on the type and number of modules needed. Merely those that select on-bounds systems also pay for the servers and other infrastructure to host the software, are ofttimes on the hook for maintenance fees and may need to eternalize their IT staffs. A hybrid model could be even more expensive, as it requires many of the resources to support on-premises ERP in addition to the subscription fees for cloud applications.
Finally, remember that the costs of ERP go beyond licensing. When calculating the TCO of various ERP solutions, factor in implementation and operating expenses related to customization, maintenance, grooming, upgrades and support. These costs will vary from one provider to the adjacent, and then practice your due diligence and ask a lot of questions to get a clear guess of the full outlay, both Capex and Opex.
History of ERP
What nosotros now refer to as ERP started in the 1960s with the invention of material requirements planning (MRP) systems. Manufacturers used MRP software to plan production schedules, make certain they had all the necessary supplies for production runs and track finished inventory. Two decades later, technology providers adult manufacturing resources planning, or MRP Ii, systems. While MRP II software still targeted manufacturers, it offered new capabilities for improved production planning.
Non until the 1990s did ERP have on its current identity equally a unified business concern direction platform. This innovative technology brought the entire business, from accounting to production development to manufacturing, social club fulfillment and HR, together on a common database. These early ERP solutions had steep capital and operating expenses. Companies needed to buy servers, hire an IT team with the appropriate expertise and and then pay for licensing and implementation. Later on that came big bills for maintenance and upgrades.
While hosted ERP solutions were available from application service providers before the advent of cloud ERP, these systems tended to exist expensive and complex.
Then, in 1998, NetSuite launched the kickoff cloud ERP. The deject operating model revolutionized this space considering it greatly reduced the upfront investment and fabricated operating costs predictable. In that location was no demand to purchase servers or hire an IT staff because the vendor managed the infrastructure and pushed out upgrades automatically.
This put ERP within accomplish of smaller companies, in turn spurring growth and profitability.
Cloud ERP has since taken off and fueled much of the innovation we've seen over the past two decades. This computing model has allowed companies to better interact both among internal departments and with external partners, sparking new insights that save businesses time and money and push them forward.
Future of ERP
Now that companies understand the tremendous benefits that come with an ERP, they're looking for means to up the game. Technology similar artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, augmented reality (AR) and the internet of things (IoT) are shaping today's ERP trends. Many of these technologies are already embedded within manufacture-leading ERP solutions.
AI and machine learning, for case, tin automate account reconciliations and flag transactions that call for a closer expect. This saves the bookkeeping team time and offloads a task most don't await frontwards to. Machine-learning applied science improves every bit information technology processes more transactions, and it can help develop more than authentic forecasts.
Blockchain packages data in a secure format and can increase transparency among companies in a supply chain. Specifically, information technology can show the condition of specific products in detail and creates an in-depth inspect trail of an item'due south journey from raw material to finished skilful. This also provides information from which the ERP can draw insights.
Augmented reality has gained a foothold in retail, allowing consumers to virtually place a rug or 3D image of a piece of furniture in their living rooms to become a sense of how it would await earlier purchasing. All the data points and images needed to make AR piece of work can be stored in the ERP.
Finally, more companies are recognizing the value of IoT devices, like sensors, scanners and cameras, that can feed information back to the ERP. A sensor that monitors the performance of a piece of warehouse automation equipment, for instance, could alert a manager when the machinery starts operating more slowly. That could be a sign the equipment is in demand of repair, and the business can arbitrate before it breaks and disrupts operations. An IoT tracker on a commitment truck could bear witness that drivers are taking inefficient routes and suggest they e'er use GPS.
Choosing the Right ERP Organisation
An ERP is a critical business concern system that must mesh with how each visitor operates, then there is no one "best" platform. Required capabilities, preferred deployment model and company size will all touch your conclusion when buying an ERP organization. Look to established vendors with proven records of success working with companies in your vertical. Always ask for reference customers, and check out success stories.
Businesses should besides consider the software provider'south roadmap for emerging technologies like IoT and blockchain.
Get-go with the modules foundational to your business and build from there. Companies often begin with a finance module to automate basic bookkeeping tasks and let leaders to easily view available greenbacks and the flow of money into and out of the organization. Products-based companies typically want to digitize inventory and order management right away considering that can generate rapid and significant savings around procurement, storage and shipping. An ecommerce awarding that plugs into the ERP is a priority for sellers that rely on this sales channel. Services organizations, on the other hand, may offset with a PSA (professional person services automation) application to simplify employee time and resources tracking and project billing.
After that, a CRM module is a prudent investment because it can improve customer communications, while supply chain management modules for manufacturing, procurement and/or warehouse direction can better align purchasing and production with need. A marketing automation solution integrated with the ERP to attract and retain customers through creative techniques may be another logical addition.
Businesses with lots of employees should add human resources direction (HRMS)/human capital direction (HCM) systems sooner rather than later to better the employee experience and earn a reputation as a great workplace.
The "right" ERP arrangement for your visitor is the one that supports your needs now and is scalable plenty to abound with your business, with modules and features that drive savings and help y'all capitalize on opportunities.
This is a big conclusion, so take the time to thoroughly evaluate all options.
Purchasing and implementing an ERP platform used to be intimidating, even overwhelming. Only the solutions available today permit companies to take it ane stride at a time and add together what they need when they need it. Never before has this software been within reach for more organizations, and leaders need to take advantage of that. An ERP has go table stakes for whatever company that wants the visibility and insights to compete and win.
ERP FAQs
What does ERP stand for?
ERP stands for enterprise resource planning, a term inquiry business firm Gartner coined in 1990 to refer to the business management platforms enterprises had begun using.
What is ERP in simple terms?
An ERP is software that businesses rely on to run and monitor the business organization performance of their daily operations. Information technology stores information from beyond the company, from finance to supply concatenation to human being resources, in a cardinal repository and can clarify and written report on all of that information.
How does ERP piece of work?
An ERP is an application that makes employ of a primal database that receives data from diverse departments inside a company. The ERP includes integrated modules defended to functions like accounting, inventory management and CRM. An ERP gives companies a unmarried identify to store, view, manage and translate data.
What is an ERP system?
ERP systems are comprised of modules that focus on certain business organization processes, such as accounting, manufacturing, and CRM. These modules role using a key database, allowing access to real-time data, and give visibility into concern functioning across these departments while minimizing information duplication. A complete ERP system will help companies upkeep, plan, and report on fiscal results.
Why is ERP used?
Companies use ERP system to connect data from multiple business concern functions within a centralized arrangement, using the same information to maintain a "single source of truth." This allows different departments to operate with the same results. Companies also salve time and money by automating manual processes and reducing opportunities for errors.
Is ERP just for finance and accounting?
While financial direction and accounting are primal ERP functions, the arrangement's capabilities stretch far across this section. Information technology can automate and ameliorate manage tasks related to purchasing, inventory and club management, manufacturing project direction, workforce management, sales and marketing and more.
Why exercise companies use ERP?
ERP software has become an invaluable tool for companies because it generates major time and cost savings. Beyond automating tasks, an ERP provides company-broad visibility and reporting that tells executives and managers where teams should focus their time and attention, which may hateful addressing pressing problems.
What's the difference between ERP and MRP?
An MRP, or fabric resources planning, system was a precursor to ERP used by manufacturers to better prepare for product runs. The manufacturing-related tasks MRP systems handled, like procurement and inventory tracking, are simply ane component of today'south ERP systems.
What is two-tier ERP?
Two-tier ERP is an arroyo that has gained traction among larger companies with subsidiaries, distinct business units or regional offices. Instead of forcing these business units or offices to utilise the legacy ERP, they run on a less-resource-intensive ERP — often a SaaS solution — that's integrated with the Tier 1 system.
What are the advantages of deject-based ERP?
Many of the advantages of deject ERP fall under lower costs and fewer headaches. A deject solution is usually cheaper and faster to implement, and post-implementation expenses may exist lower because the vendor takes intendance of all maintenance and upgrades. A cloud-based system can likewise seamlessly support your growth, as the vendor manages all hardware.
Source: https://www.netsuite.com/portal/resource/articles/erp/what-is-erp.shtml
Post a Comment for "(B) What Methods Have Been Used to Address the Erp System?"